Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson
4.9 (341) · $ 26.99 · In stock
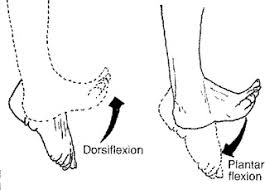
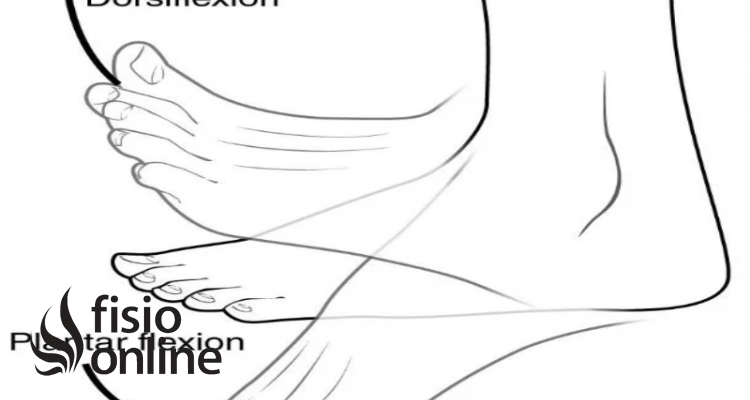
Download scientific diagram | Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson [6], the medial and lateral malleolus and the strong collateral ligaments stabilize the articulation allowing little or no lateral motion. For Lehmkuhl and Smith [7], the lateral malleolus is projected more distally than the medial one. Thus, the lateral motion of the ankle is more limited than the medial movement. This characterizes a specific axis of movement of the ankle (Figure 3). from publication: Modelling of the Human Ankle by means of a Nonlinear Oscillators System | A Nonlinear oscillators system can simulate the behaviour of the main elements involved in the human locomotion, as example, the ankle. These oscillators can be used in control systems of locomotion as pattern generators similar to the human gait pattern, providing approach | Ankle Joint, Oscillators and Nonlinear | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson [6]

Biomechanics of the natural, arthritic, and replaced human ankle joint - Leardini - 2014 - Journal of Foot and Ankle Research - Wiley Online Library

Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson [6]

Ankle Power and Endurance Outcomes Following Isolated Gastrocnemius Recession for Achilles Tendinopathy - Deborah A. Nawoczenski, Frank E. DiLiberto, Maxwell S. Cantor, Josh M. Tome, Benedict F. DiGiovanni, 2016

Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson [6]

Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson [6]
Improving Plantar Flexion - Get Better, Faster

Auxiliary Movements

Plantarflexion - Morphopedics

Running temporal parameters and vertical tibial acceleration. * denotes
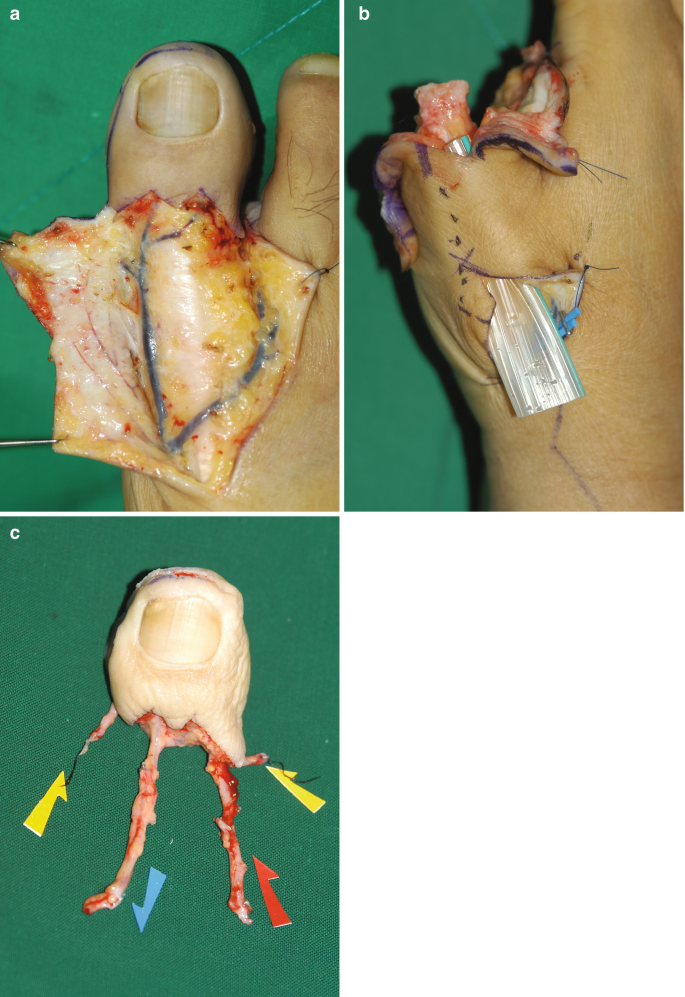
Microsurgical Reconstruction

Auxiliary Movements

PDF) Study and Modeling of the Ankles Movement Pattern in the Course of Human Locomotion
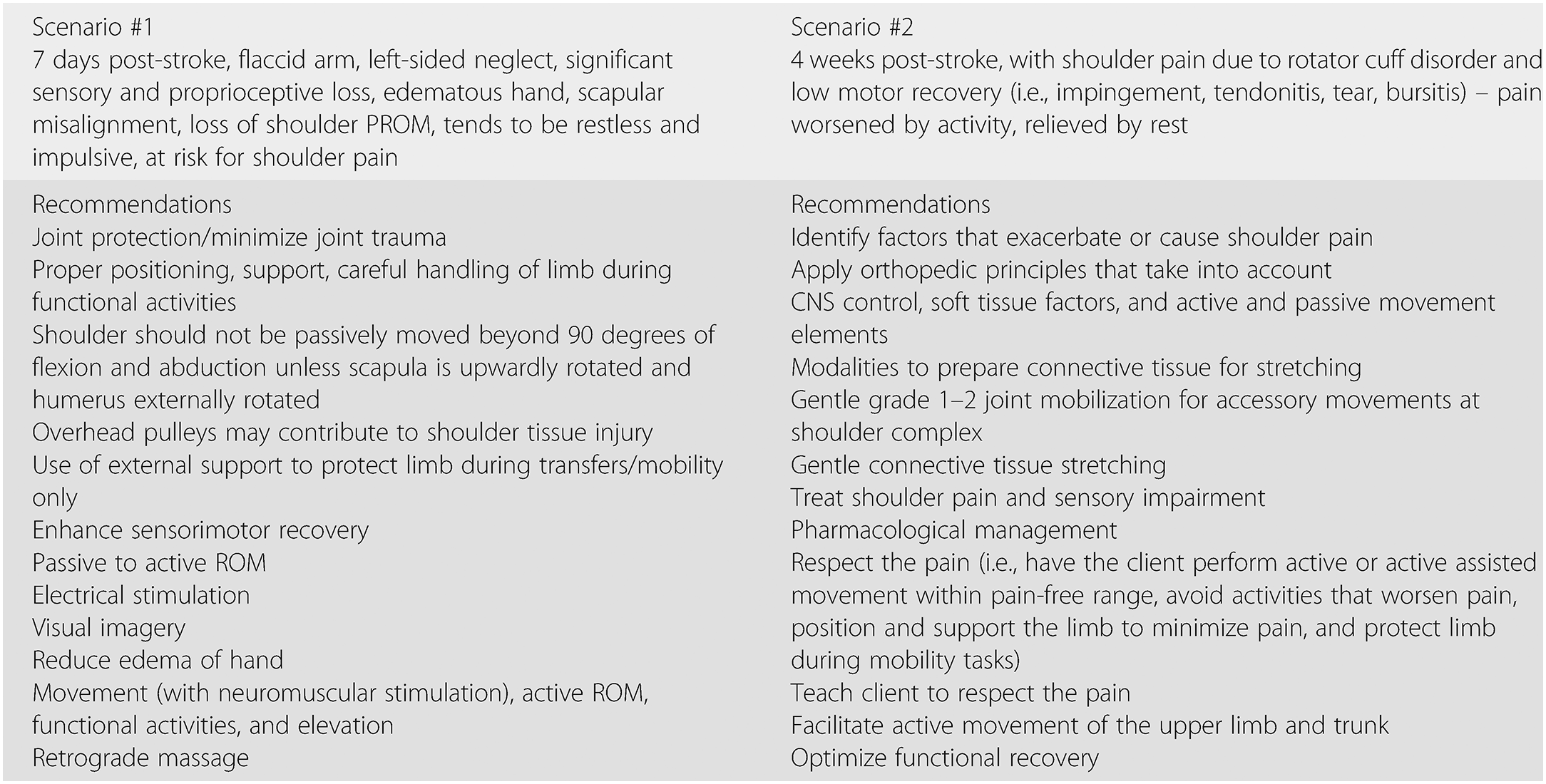
Symptom-specific neurorehabilitation: sensory and motor dysfunctions (Section 4) - Textbook of Neural Repair and Rehabilitation






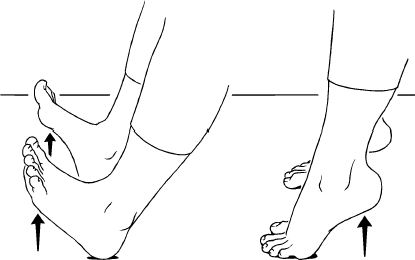


:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/plantar-flexion-of-foot/pSP4hyc58sLLh4sFnHH7Q_Plantar_flexion__of_foot_.png)
![Plantar flexion e dorsal flexion [5]. According Bates and Hanson](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301654404/figure/fig2/AS:355330174275587@1461728723815/Plantar-flexion-e-dorsal-flexion-5-According-Bates-and-Hanson-6-the-medial-and.png)