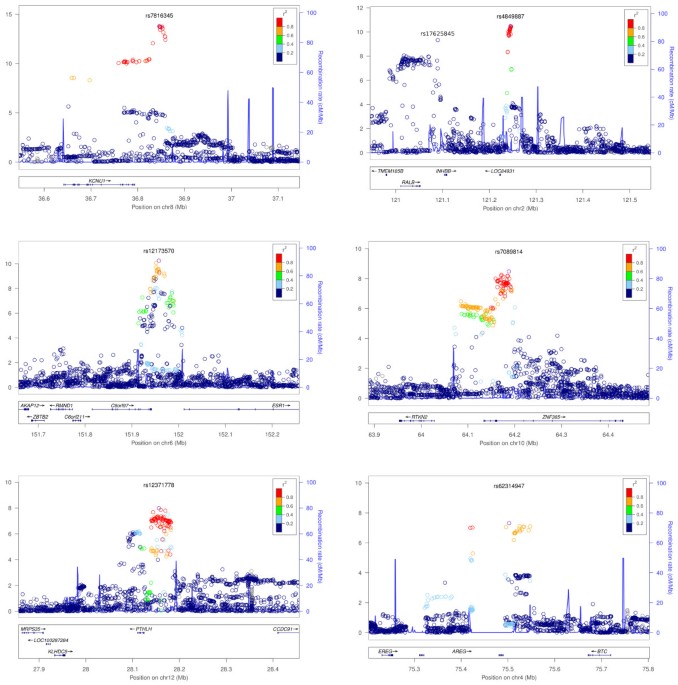
Genetic variants associated with breast size also influence breast
4.7 (375) · $ 6.50 · In stock
Background While some factors of breast morphology, such as density, are directly implicated in breast cancer, the relationship between breast size and cancer is less clear. Breast size is moderately heritable, yet the genetic variants leading to differences in breast size have not been identified. Methods To investigate the genetic factors underlying breast size, we conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of self-reported bra cup size, controlling for age, genetic ancestry, breast surgeries, pregnancy history and bra band size, in a cohort of 16,175 women of European ancestry. Results We identified seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) significantly associated with breast size (p<5·10−8): rs7816345 near ZNF703, rs4849887 and (independently) rs17625845 flanking INHBB, rs12173570 near ESR1, rs7089814 in ZNF365, rs12371778 near PTHLH, and rs62314947 near AREG. Two of these seven SNPs are in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with SNPs associated with breast cancer (those near ESR1 and PTHLH), and a third (ZNF365) is near, but not in LD with, a breast cancer SNP. The other three loci (ZNF703, INHBB, and AREG) have strong links to breast cancer, estrogen regulation, and breast development. Conclusions These results provide insight into the genetic factors underlying normal breast development and show that some of these factors are shared with breast cancer. While these results do not directly support any possible epidemiological relationships between breast size and cancer, this study may contribute to a better understanding of the subtle interactions between breast morphology and breast cancer risk.

A Population-Based Study of Genes Previously Implicated in Breast Cancer

Genetics linked to breast size and breast cancer risk - 23andMe Blog

PDF) Genetic variants associated with motion sickness point to roles for inner ear development, neurological processes, and glucose homeostasis

Assessment of the prognostic role of a 94-single nucleotide polymorphisms risk score in early breast cancer in the SIGNAL/PHARE prospective cohort: no correlation with clinico-pathological characteristics and outcomes, Breast Cancer Research
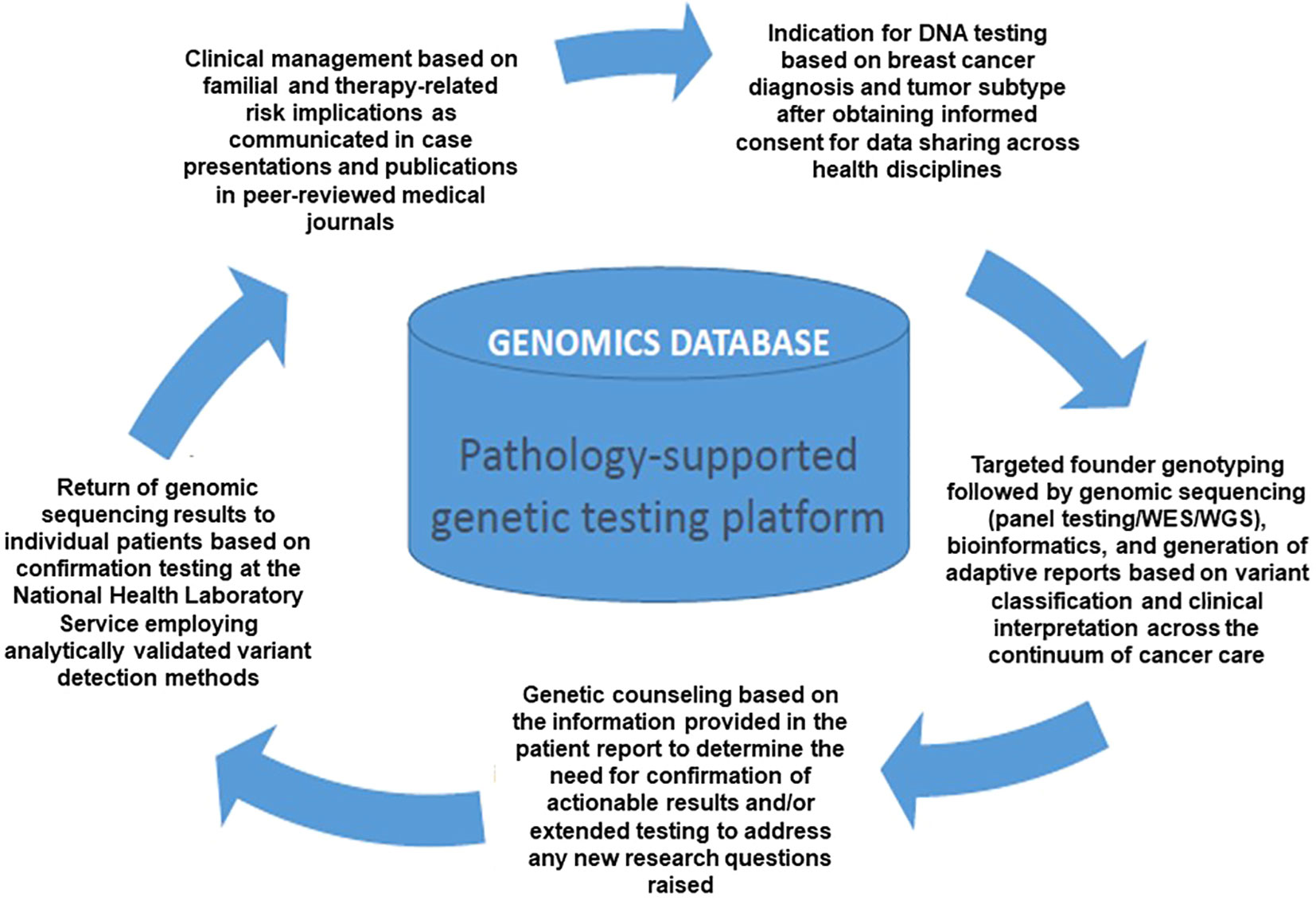
Frontiers Implementation of multigene panel testing for breast and ovarian cancer in South Africa: A step towards excellence in oncology for the public sector

Deciphering how early life adiposity influences breast cancer risk using Mendelian randomization
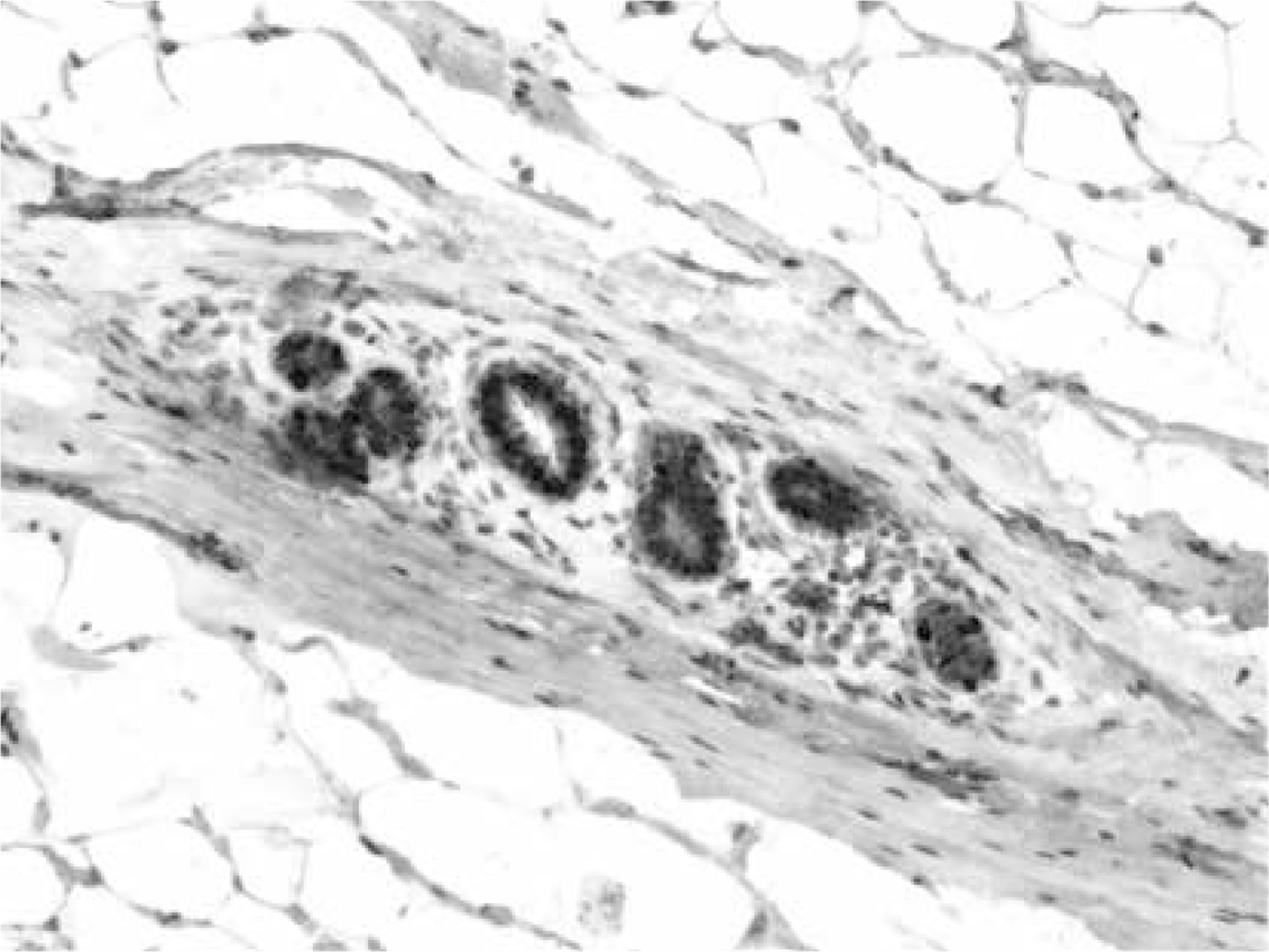
The role of oestrogen and progesterone receptors in gigantomastia

Average Breast Size: Are Age, Height, and Weight a Factor?

The genetic interplay between body mass index, breast size and breast cancer risk: a Mendelian randomization analysis. - Abstract - Europe PMC
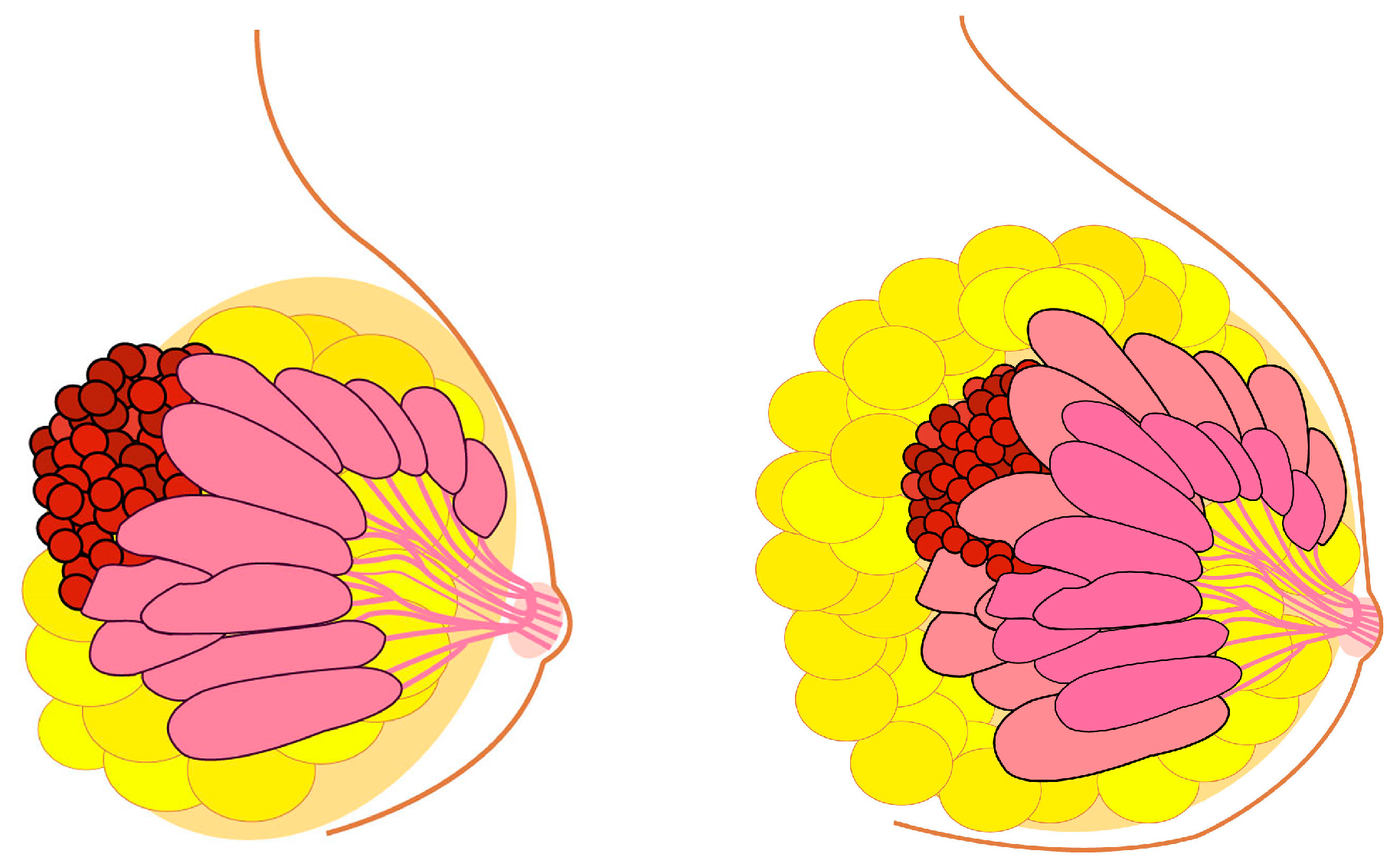
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text